Understanding ISO 31000 Risk Management and Its Key Benefits
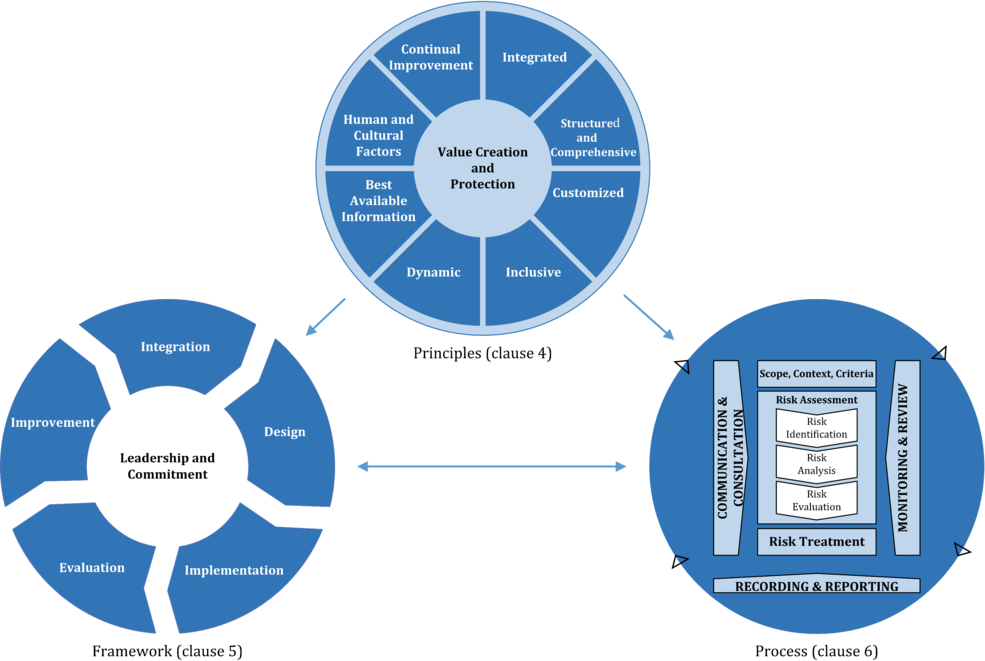
Risk management is one important aspect of organizational success in this complex business environment. The ISO 31000 risk management is all-inclusive and helps an organization in the systematic approach towards the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks. It provides an international standard on how to manage uncertainties that can be a threat to the objectives set for organizations that offer a structured approach to such potential challenges in life.
Key Principles of Risk Management
Good management risk is more significant and goes beyond pure problem prevention. The ISO 31000 offers a holistic, integrated approach so that risk becomes part of decision-making processes; it is viewed as a dynamic integral to the firm’s strategy on operational matters. From this perspective, organizations can advance more resilient strategies and adapt quickly by integrating strong methodology through organizational core operational systems.
Comprehensive Framework for Organizations
The standard provides a broad framework applicable in various industries and types of organizations. It allows organizations to follow a flexible set of guidelines that could suit their particular organizational needs and would still remain basic to core principles of risk management. It becomes possible for more complex forms of identification, analysis, and remediation of identified risks, in order to impact the strategy and operation.
Integration with Organizational Processes
Organizational processes must be embedded to successfully manage risks. The ISO 31000 standard guides organizations on how to embed risk considerations into strategic planning, operational management, and general organizational governance. This approach will ensure that the organization integrates risk management into its organizational culture rather than as a stand-alone activity.
Risk Identification and Analysis
The standard offers comprehensive methodologies for identifying and analyzing potential risks across various organizational domains. It encourages a systematic approach to risk assessment that considers both internal and external factors that might impact organizational performance. Organizations can develop more nuanced and sophisticated risk identification strategies that go beyond traditional risk management approaches.
Continuous Improvement Approach
ISO 31000 fosters a culture of continuous improvement in risk management practices. The standard stresses the importance of continuous review, monitoring, and adjustment of risk management practices. Organizations can thus evolve more responsive and adaptive approaches to handling uncertainties and ensure that their risk management processes are effective in the evolving business environments.
International Acceptance and Repute
The International Organization for Standardization 31000 framework provides risk management guidelines that are recognized globally. Organizations that implement these standards will be considered as dedicated to best practices and professional risk management, thus enhancing organizational credibility and providing a competitive advantage in ever increasingly complex global business landscapes with economic and operational benefits.
The ISO 31000 risk management approaches have a lot of economic and operational benefits. Organizations can reduce the potential financial losses, improve resource allocation, and create more stable operational environments. The standard helps businesses develop more resilient strategies that can effectively navigate uncertainties and potential challenges.
Technology and Risk Management
The convergence of modern risk management is ever-increasingly in tandem with technological advances. By the ISO 31000 standard, there is a guideline in managing technologically integrated risks of digital transformation and emerging technological challenges. Organizations can develop more inclusive approaches in understanding and responding to these issues.
Industry-Specific Applications
The ISO 31000 standard can be tailored to suit the needs of different industries in addressing specific risk management issues. Manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, and technology sectors can tailor the framework to meet their specific operational requirements while maintaining core risk management principles. This flexibility ensures the standard remains relevant across diverse business environments.
Organizational Culture and Risk Awareness
Moving the ISO 31000 into action involves more than technical processes because the standard facilitates a risk-conscious organisational culture whereby there is a change of mindset concerning risk management throughout all the groups. This sets up more accountable and proactive corporate cultures that help to detect issues in good time.
Training and Implementation
ISO 31000 implementation requires thorough training and organizational support. Leadership needs to support the risk management programs by providing adequate resources and building a risk-informed culture at all levels of the organization. Effective implementation calls for developing high-quality training programs and establishing open channels of communication.
Communication and Reporting Mechanisms
Robust communication and reporting are the bases for effective risk management. According to the ISO 31000 standard, organizations should establish clear, transparent, and comprehensive reporting mechanisms that facilitate sharing of risk-related information at all levels. Communication frameworks in place ensure that stakeholders understand the risk, mitigation, and ongoing efforts of risk management within the organization. This helps foster a more informed and proactive approach to organizational decision-making.
Stakeholder Engagement and Risk Management
Effective risk management requires interaction with other stakeholders. The ISO 31000 standard promotes organizations to adopt more inclusive approaches that are sensitive to views from different levels of the organization and external partners. In this regard, businesses can utilize diverse perspectives in collaborative risk assessment processes to identify risks better and develop more holistic mitigation strategies that take into account a wider range of experiences and expertise.
Ethical Issues in Risk Management
Risk management extends beyond technical processes to include ethical considerations. The ISO 31000 standard promotes approaches that balance organizational objectives with broader social responsibilities. This framework encourages businesses to consider the potential broader impacts of their risk management strategies, ensuring that risk mitigation efforts align with ethical standards and contribute positively to organizational and societal well-being.
Psychological Aspects of Risk Perception
The psychological dimensions of risk perception must be understood to be able to manage them properly. ISO 31000 does acknowledge that human aspects are included in risk assessment and may have cognitive biases. The risk management approaches that are developed would become more sensitive, and comprehensive strategies could be produced in order to mitigate the risks better. It is now about the future of risk management.
Risk management will only evolve with business environments becoming increasingly complex. ISO 31000 represents a dynamic framework that keeps abreast with changes in the technological, economic, and social environment. Innovative organizations realize the significance of holistic approaches to risk management for sustainable success.
Conclusion
Organizations looking to build their risk management capabilities can leverage the implementation of ISO 31000 guidelines, which are thorough frameworks that would help organizations implement robust strategies through which they may navigate organizational uncertainties. For expertise and support in gaining ISO 31000 certification, businesses can count on INTERCERT, a company that specializes in Management System Certification.